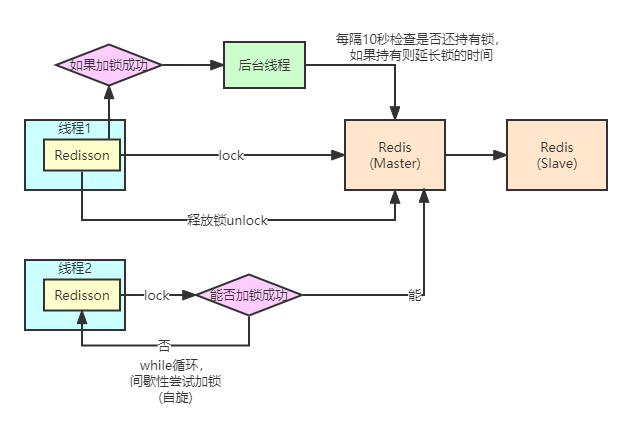
Redisson 分布式锁原理
1. 工具类
package com.meta.mall.common.utils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* redisson 分布式工具类
*
* @author gaoyang
* @date 2022-05-14 08:58
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class RedissonUtils {
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
/**
* 加锁
*
* @param lockKey
*/
public void lock(String lockKey) {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
lock.lock();
}
/**
* 带过期时间的锁
*
* @param lockKey key
* @param leaseTime 上锁后自动释放锁时间
*/
public void lock(String lockKey, long leaseTime) {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
lock.lock(leaseTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 带超时时间的锁
*
* @param lockKey key
* @param leaseTime 上锁后自动释放锁时间
* @param unit 时间单位
*/
public void lock(String lockKey, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
lock.lock(leaseTime, unit);
}
/**
* 尝试获取锁
*
* @param lockKey key
* @return
*/
public boolean tryLock(String lockKey) {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
return lock.tryLock();
}
/**
* 尝试获取锁
*
* @param lockKey key
* @param waitTime 最多等待时间
* @param leaseTime 上锁后自动释放锁时间
* @return boolean
*/
public boolean tryLock(String lockKey, long waitTime, long leaseTime) {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
try {
return lock.tryLock(waitTime, leaseTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("RedissonUtils - tryLock异常", e);
}
return false;
}
/**
* 尝试获取锁
*
* @param lockKey key
* @param waitTime 最多等待时间
* @param leaseTime 上锁后自动释放锁时间
* @param unit 时间单位
* @return boolean
*/
public boolean tryLock(String lockKey, long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
try {
return lock.tryLock(waitTime, leaseTime, unit);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("RedissonUtils - tryLock异常", e);
}
return false;
}
/**
* 释放锁
*
* @param lockKey key
*/
public void unlock(String lockKey) {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
lock.unlock();
}
/**
* 是否存在锁
*
* @param lockKey key
* @return
*/
public boolean isLocked(String lockKey) {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
return lock.isLocked();
}
}
2. lock和tryLock的区别
1.返回值
- lock 是 void;
- tryLock 是 boolean。
2.时机
- lock 一直等锁释放;
- tryLock 获取到锁返回true,获取不到锁并直接返回false。
lock拿不到锁会一直等待。tryLock是去尝试,拿不到就返回false,拿到返回true。
tryLock是可以被打断的,被中断的,lock是不可以。
3. 源码分析
3.1 lock
private void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, boolean interruptibly) throws InterruptedException {
// 获取当前线程 ID
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
// 获取锁,正常获取锁则ttl为null,竞争锁时返回锁的过期时间
Long ttl = tryAcquire(-1, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
return;
}
// 订阅锁释放事件
// 如果当前线程通过 Redis 的 channel 订阅锁的释放事件获取得知已经被释放,则会发消息通知待等待的线程进行竞争
RFuture future = subscribe(threadId);
if (interruptibly) {
commandExecutor.syncSubscriptionInterrupted(future);
} else {
commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
}
try {
while (true) {
// 循环重试获取锁,直至重新获取锁成功才跳出循环
// 此种做法阻塞进程,一直处于等待锁手动释放或者超时才继续线程
ttl = tryAcquire(-1, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
break;
}
// waiting for message
if (ttl >= 0) {
try {
future.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
if (interruptibly) {
throw e;
}
future.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
} else {
if (interruptibly) {
future.getNow().getLatch().acquire();
} else {
future.getNow().getLatch().acquireUninterruptibly();
}
}
}
} finally {
// 最后释放订阅事件
unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
// get(lockAsync(leaseTime, unit));
}
RFuture tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand command) {
return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.singletonList(getRawName()), unit.toMillis(leaseTime), getLockName(threadId));
}
此段脚本为一段lua脚本:
KEY[1]: 为你加锁的lock值
ARGV[2]: 为线程id
ARGV[1]: 为设置的过期时间
第一个if:
- 判断是否存在设置lock的key是否存在,不存在则利用redis的hash结构设置一个hash,值为1,并设置过期时间,后续返回锁。
第二个if:
- 判断是否存在设置lock的key是否存在,存在此线程的hash,则为这个锁的重入次数加1(将hash值+1),并重新设置过期时间,后续返回锁。
最后返回:
- 这个最后返回不是说最后结果返回,是代表以上两个if都没有进入,则代表处于竞争锁的情况,后续返回竞争锁的过期时间。
3.2 tryLock
tryLock具有返回值,true或者false,表示是否成功获取锁。
tryLock前期获取锁逻辑基本与lock一致,主要是后续获取锁失败的处理逻辑与lock不一致。
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
}
// 获取锁失败后,中途tryLock会一直判断中间操作耗时是否已经消耗锁的过期时间,如果消耗完则返回false
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId);
// 将订阅阻塞,阻塞时间设置为我们调用tryLock设置的最大等待时间,超过时间则返回false
if (!subscribeFuture.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) {
subscribeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
});
}
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
try {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time = 0 && ttl
应尽量使用tryLock,且携带参数,因为可设置最大等待时间以及可及时获取加锁返回值,后续可做一些其他加锁失败的业务
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持IT俱乐部。

