SpringSecurity 集成第三方登录
认证及自定义流程
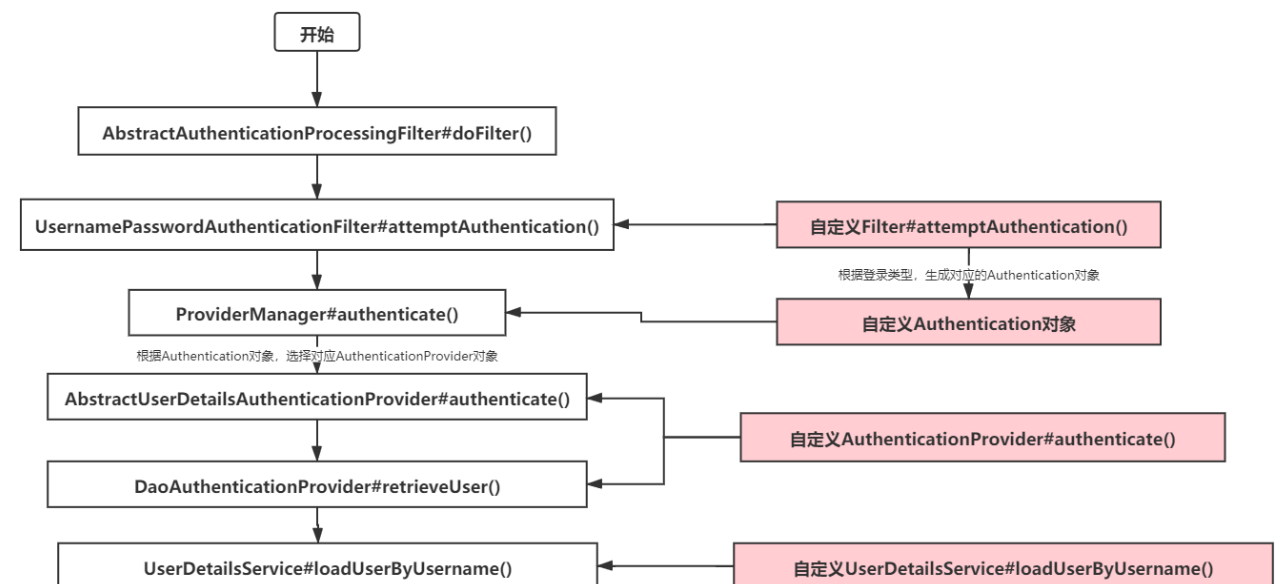
首先我们提供一个实现了AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter抽象类的过滤器,用来代替UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter逻辑,然后提供一个AuthenticationProvider实现类代替AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider或DaoAuthenticationProvider,最后再提供一个UserDetailsService实现类。
1.验证码登录
1.通用过滤器实现–ThirdAuthenticationFilter
这个ThirdAuthenticationFilter过滤器我们可以仿照UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter来实现(也实现了AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter抽象类),主要是重新定义了attemptAuthentication()方法,这里需要根据“authType”参数值的类别构建不同的AbstractAuthenticationToken,具体实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | //验证类型,比如Sms,uernamepassword等 private String authTypeParameter = "authType"; //对应用户名或手机号等 private String principalParameter = "principal"; //对应密码或验证码等 private String credentialsParameter = "credentials"; private boolean postOnly = true; public ThirdAuthenticationFilter() { super(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/login/doLogin", "POST")); } @Override public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException, IOException, ServletException { if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) { throw new AuthenticationServiceException( "Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod()); } String authType = request.getParameter(authTypeParameter); if(StringUtils.isEmpty(authType)){ authType = AuthTypeEnum.AUTH_TYPE_DEFAULT.getAuthType(); } String principal = request.getParameter(principalParameter); String credentials = request.getParameter(credentialsParameter); AbstractAuthenticationToken authRequest = null; switch (authType){ case "sms": authRequest = new SmsAuthenticationToken(principal, credentials); ((SmsAuthenticationToken)authRequest).setCode((String)request.getSession().getAttribute("code")); break; case "github": authRequest = new GithubAuthenticationToken(principal, credentials); break; case "default": authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal, credentials); } authRequest.setDetails(authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request)); return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest); }} |
定义了ThirdAuthenticationSecurityConfig 配置类,我们还需要在SpringSecurity配置类中应用才能生效,具体实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | @Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/error","/login/**","/login/goLogin","/login/doLogin","/login/code","/login/authorization_code").anonymous() .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .formLogin() .loginPage("/login/goLogin") .loginProcessingUrl("/login/doLogin") .failureUrl("/login/error") .permitAll() .successHandler(new QriverAuthenticationSuccessHandler("/index/toIndex")); //这里我们省略了一些配置 …… //应用前面定义的配置 http.apply(thirdAuthenticationSecurityConfig);} |
至此,我们定义的通用第三方过滤器就完成了,并且也完成了在SpringSecurity中生效的配置。下面我们就开始分别实现不同类型登录的具体过程。
在ThirdAuthenticationFilter 类的attemptAuthentication()方法中,我们通过authType类型,然后创建对应的Authentication实现来实现不同方式的登录,这里我们主要实现了如下三种方式,我们分别梳理一下。
3、默认的登录过程
默认的登录过程,即根据用户名密码进行登录,需要使用到UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,当“authType”参数为”default”时,这里就会创建UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken对象,然后后续通过ProviderManager的authenticate()方法,最后就会调用AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider(DaoAuthenticationProvider)的 authenticate()方法,最终又会调用定义的UserDetailsService实现类。这是默认的过程,这里就不再重复其中的逻辑,除了UserDetailsService实现类需要自己定义,其他都是SpringSecurity提供的实现类。
4、短信验证码登录实现
短信验证码登录,是最贴近用户名密码登录的一种方式,所以我们完全可以仿照用户名密码这种方式实现。我们这里先梳理一下短信验证码登录的业务逻辑:首先,登录界面输入手机号码,然后再点击“获取验证码”按钮获取短信验证码,然后输入收到的短信验证码,最后点击“登录”按钮进行登录认证。和用户名密码登录相比,短信验证码登录多了一个获取验证码的过程,其他其实都是一样的,我们下面逐步实现短信验证码登录:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | @RestController@RequestMapping("/login")public class SmsValidateCodeController { //生成验证码的实例对象 @Autowired private ValidateCodeGenerator smsCodeGenerator; //调用服务商接口,发送短信验证码的实例对象 @Autowired private DefaultSmsCodeSender defaultSmsCodeSender; @RequestMapping("/code") public String createSmsCode(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletRequestBindingException { ValidateCode smsCode = smsCodeGenerator.generate(new ServletWebRequest(request)); String mobile = (String)request.getParameter("principal"); request.getSession().setAttribute("code",smsCode.getCode()); defaultSmsCodeSender.send(mobile, smsCode.getCode()); System.out.println("验证码:" + smsCode.getCode()); return "验证码发送成功!"; }} |
在上述方法中,我们注入了smsCodeGenerator和defaultSmsCodeSender两个实例对象,分别用来生成验证码和发送短信验证码,这个可以根据项目的实际情况进行定义和实现,这里不再贴出其中的实现。同时在createSmsCode()方法中,还有一点需要注意的就是,我们发出去的短信验证码需要进行保存,方便后续登录时进行验证,这个也可以选择很多方法,比如说会话、数据库、缓存等,我这里为了简单,直接存到了session会话中了。
然后,我们前面定义ThirdAuthenticationFilter过滤器时,根据登录方式不同,需要对应的Authentication对象,这里我们还需要创建短信验证登录需要的Authentication类,这里我们可以仿照UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken类进行编写,实现如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | public class SmsAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken { //对应手机号码 private final Object principal; //对应手机验证码 private Object credentials; //后台存储的短信验证码,用于验证前端传过来的是否正确 private String code; public SmsAuthenticationToken(String mobile, Object credentials){ super(null); this.principal = mobile; this.credentials = credentials; this.code = code; setAuthenticated(false); } public SmsAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Collection extends GrantedAuthority> authorities, Object credentials){ super(authorities); this.principal = principal; this.credentials = credentials; super.setAuthenticated(true); } @Override public Object getCredentials() { return this.credentials; } @Override public Object getPrincipal() { return this.principal; } public void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException { if (isAuthenticated) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Cannot set this token to trusted - use constructor which takes a GrantedAuthority list instead"); } super.setAuthenticated(false); } public String getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(String code) { this.code = code; } @Override public void eraseCredentials() { super.eraseCredentials(); credentials = null; }} |
在SmsAuthenticationToken 类中,我们增加了一个code属性,其实该属性不是必须的,我这里是为了方便传递存储在session会话中的验证码而添加的,如果使用缓存或数据库进行存储验证码,该属性就可以省略。
在AuthenticationManager的authenticate()方法中,会根据Authentication类型选择AuthenticationProvider对象,所以我们这里自定义短信验证码需要的AuthenticationProvider对象,实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | @Componentpublic class SmsAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider{ @Autowired @Qualifier("smsUserDetailsService") private UserDetailsService userDetailsService; @Override public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException { SmsAuthenticationToken token = (SmsAuthenticationToken) authentication; String mobile = (String)token.getPrincipal(); //首先,验证验证码是否正确 String code = (String)token.getCredentials(); String sCode = token.getCode(); if(StringUtils.isEmpty(code) || !code.equalsIgnoreCase(sCode)){ throw new BadCredentialsException("手机验证码错误(Bad credentials),请重试!"); } //然后,查询对应用户 UserDetails user = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(mobile); if (Objects.isNull(user)) { throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException("根据手机号:" + mobile + ",无法获取对应的用户信息!"); } SmsAuthenticationToken authenticationResult = new SmsAuthenticationToken(user.getUsername(), user.getAuthorities(), token.getCredentials()); authenticationResult.setDetails(token.getDetails()); return authenticationResult; } @Override public boolean supports(Class> authentication) { return SmsAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication); }} |
在SmsAuthenticationProvider 中,supports()方法决定了该实例对象仅支持SmsAuthenticationToken对象的验证。同时,根据authenticate()方法传递参数authentication对象(包括了登录信息:手机号和验证码,session存储的验证码),我们这里session存储的验证码,是因为我们采用了会话存储的方式,如果使用数据库,我们这里就可以通过手机号,去数据库或缓存查询对应的验证码,然后和authentication对象传递过来的验证码进行比对,验证成功,说明登录认证成功,否则登录认证失败。登录成功后,我们就可以调用userDetailsService对象的loadUserByUsername()方法获取登录用户的其他相关信息(权限等),具体实现在自定义的SmsUserDetailsService类中实现,具体如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | @Component("smsUserDetailsService")public class SmsUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SmsUserDetailsService.class); @Autowired private SysUserService sysUserService; @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { //1、查询用户信息 SysUser user = new SysUser(); user.setMobile(username); SysUser qUser = sysUserService.getOne(new QueryWrapper(user),true); if(qUser == null) { logger.info("手机号为”" + username + "“的用户不存在!!!"); throw new UsernameNotFoundException("手机号为”" + username + "“的用户不存在!!!"); } //2、封装用户角色 UserRole userRole = sysUserService.getRoleByUserId(qUser.getId()); Collection authorities = new ArrayList(); authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(String.valueOf(userRole.getRoleId()))); return new LoginUser(qUser.getUsername(), qUser.getPassword(),authorities); } } |
2.GitHub登录
和短信验证码登录认证相比,Github登录又会有自己的特殊性,我们这里先梳理一下基于Github进行登录验证的大致逻辑:首先,点击Github登录认证按钮,然后会跳转到github登录界面,输入github系统的用户名密码,登录成功,就会跳转到我们自己的系统中的首页。和基于用户名密码的登录方式相比,Github登录不需要类似用户名和密码这样的输入(在自己的系统中),同时又需要根据获取到的github用户信息,换取在自己系统对应的用户信息。具体实现步骤如下:
在github的配置省略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | @Controller@RequestMapping("/login")public class GithubValidateController { @Autowired private GithubClientService githubClientService; @RequestMapping("/authorization_code") public void authorization_code(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String code) throws ServletRequestBindingException, IOException { //github登录验证,并获取access_token Map resp = githubClientService.queryAccessToken(code); //跳转本系统的登录流程,获取用户信息,实现两个系统用户的对接 this.sendByPost(response, url,resp.get("access_token"),"github"); //this.sendByPost(response, url,"access_token","github"); } public void sendByPost(HttpServletResponse response,String url, String principal, String authType) throws IOException { response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println(""-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">"); out.println(""); out.println(" <title>Post 方法</title>"); out.println(" "); out.println(""); out.println(""); out.println(""); out.println(""); out.println("window.document.submitForm.submit(); "); out.println(" "); out.println(""); out.flush(); out.close(); }} |
“/login/authorization_code”接口对应了我们在Github中配置的回调函数,即在Github登录验证成功后,就会回调该接口,我们就是就在回调方法中,模拟了用户名密码登录的方式,调用了SpringSecurity登录认证需要的“/login/doLogin”接口。这里,我们通过queryAccessToken()方法根据回调传递的code获取对应的accessToken,然后把accessToken作为登录使用的principal 参数值,之而立不需要传递密码,因为我们经过Github授权,就可以认为完成了登录认证的判断过程了。
其中GithubClientService类,提供了获取accessToken和用户信息的两个方法,具体实现方式如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | @Servicepublic class GithubClientService { //前面在github中配置时产生的 private String clientId = "######"; private String clientSecret = "######"; private String state = "123"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @Nullable private WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext; //获取accessToken public Map queryAccessToken(String code ){ Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("client_id", clientId); map.put("client_secret", clientSecret); map.put("state", state); map.put("code", code); map.put("redirect_uri", redirectUri); Map resp = restTemplate.postForObject("https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token", map, Map.class); return resp; } //获取用户信息 public Map queryUser(String accessToken){ HttpHeaders httpheaders = new HttpHeaders(); httpheaders.add("Authorization", "token " + accessToken); HttpEntity> httpEntity = new HttpEntity(httpheaders); ResponseEntity<map> exchange = restTemplate.exchange("https://api.github.com/user", HttpMethod.GET, httpEntity, Map.class); System.out.println("exchange.getBody() = " + exchange.getBody()); return exchange == null ? null : exchange.getBody(); }}</map> |
其实,完成了上述的配置和方式后,后续的方式就和短信验证码的逻辑一样了,这里我们简要的再梳理一下。
首先,我们也需要定义一个基于Github登录需要的Authentication实现类,具体实现和前面的SmsAuthenticationToken类似,这里不再重复贴代码了。
然后,我们再定义一个AuthenticationProvider实现类GithubAuthenticationProvider,具体实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | @Componentpublic class GithubAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider{ @Autowired @Qualifier("githubUserDetailsService") private UserDetailsService userDetailsService; @Autowired private GithubClientService githubClientService; @Override public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException { GithubAuthenticationToken token = (GithubAuthenticationToken) authentication; String accessToken = (String)token.getPrincipal(); //根据accessToken 获取github用户信息 Map userInfo = githubClientService.queryUser(accessToken); //然后,根据github用户,查询对应系统用户信息 UserDetails user = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername((String)userInfo.get("login")); if (Objects.isNull(user)) { throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException("根据accessToken:" + accessToken + ",无法获取对应的用户信息!"); } GithubAuthenticationToken authenticationResult = new GithubAuthenticationToken(user.getUsername(), user.getAuthorities(), token.getCredentials()); authenticationResult.setDetails(token.getDetails()); return authenticationResult; } @Override public boolean supports(Class> authentication) { return GithubAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication); }} |
在GithubAuthenticationProvider 类的authenticate()方法中,参数authentication中对应的是Github授权后传递的accessToken值,我们这里需要根据accessToken值换取Github用户信息,这里通过queryUser()方法实现,然后根据github用户名去获取对应的系统用户信息。如果根据github用户名用户获取的系统用户为空,我们可以根据自己的需求,自动生成一个用户或者跳转到注册页面,让用户注册一个页面,这里为了简单,我们直接抛出了一个异常。
关于自定义UserDetailsService实现类,主要需要实现根据github用户名查询对应系统用户的功能
当认证完成后要返回token可以实现AuthenticationSuccessHandler
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication; import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; public class CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler { private final JwtTokenProvider jwtTokenProvider; // 假设你有一个JwtTokenProvider类来生成JWT public CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler(JwtTokenProvider jwtTokenProvider) { this.jwtTokenProvider = jwtTokenProvider; } @Override public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException { // 生成JWT String token = jwtTokenProvider.generateToken(authentication); // 将JWT添加到响应头中 response.setHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + token); // 或者将JWT添加到响应体中(取决于你的API设计) // response.getWriter().write(token); response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK); } } |
并在securityconfig中设置
到此这篇关于SpringSecurity集成第三方登录的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringSecurity登录内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

