1.什么是kubernetes?
Kubernetes(也称 k8s 或 “kube”)是一个开源的容器编排平台,可以自动化在部署、管理和扩展容器化应用过程中涉及的许多手动操作。 Kubernetes 最初是由 Google 工程师作为 Borg 项目开发和设计的,后于 2015 年捐赠给 云原生计算基金会(CNCF)。红帽® 是第一批与 Google 合作研发 Kubernetes 的公司之一,作为 Kubernetes 上游项目的第二大贡献者,我们甚至在这个项目启动之前就已参与其中。
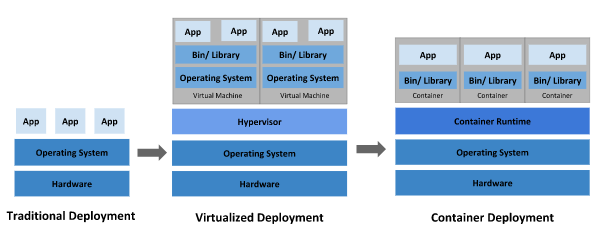
传统部署时代:
早期,各个组织是在物理服务器上运行应用程序。 由于无法限制在物理服务器中运行的应用程序资源使用,因此会导致资源分配问题。 例如,如果在同一台物理服务器上运行多个应用程序, 则可能会出现一个应用程序占用大部分资源的情况,而导致其他应用程序的性能下降。 一种解决方案是将每个应用程序都运行在不同的物理服务器上, 但是当某个应用程序资源利用率不高时,剩余资源无法被分配给其他应用程序, 而且维护许多物理服务器的成本很高。
虚拟化部署时代:
因此,虚拟化技术被引入了。虚拟化技术允许你在单个物理服务器的 CPU 上运行多台虚拟机(VM)。 虚拟化能使应用程序在不同 VM 之间被彼此隔离,且能提供一定程度的安全性, 因为一个应用程序的信息不能被另一应用程序随意访问。 虚拟化技术能够更好地利用物理服务器的资源,并且因为可轻松地添加或更新应用程序, 而因此可以具有更高的可扩缩性,以及降低硬件成本等等的好处。 通过虚拟化,你可以将一组物理资源呈现为可丢弃的虚拟机集群。 每个 VM 是一台完整的计算机,在虚拟化硬件之上运行所有组件,包括其自己的操作系统。
容器部署时代:
容器类似于 VM,但是更宽松的隔离特性,使容器之间可以共享操作系统(OS)。 因此,容器比起 VM 被认为是更轻量级的。且与 VM 类似,每个容器都具有自己的文件系统、CPU、内存、进程空间等。 由于它们与基础架构分离,因此可以跨云和 OS 发行版本进行移植。 容器因具有许多优势而变得流行起来,例如:
- 敏捷应用程序的创建和部署:与使用 VM 镜像相比,提高了容器镜像创建的简便性和效率。
- 持续开发、集成和部署:通过快速简单的回滚(由于镜像不可变性), 提供可靠且频繁的容器镜像构建和部署。
- 关注开发与运维的分离:在构建、发布时创建应用程序容器镜像,而不是在部署时, 从而将应用程序与基础架构分离。
- 可观察性:不仅可以显示 OS 级别的信息和指标,还可以显示应用程序的运行状况和其他指标信号。
- 跨开发、测试和生产的环境一致性:在笔记本计算机上也可以和在云中运行一样的应用程序。
- 跨云和操作系统发行版本的可移植性:可在 Ubuntu、RHEL、CoreOS、本地、 Google Kubernetes Engine 和其他任何地方运行。
- 以应用程序为中心的管理:提高抽象级别,从在虚拟硬件上运行 OS 到使用逻辑资源在 OS 上运行应用程序。
- 松散耦合、分布式、弹性、解放的微服务:应用程序被分解成较小的独立部分, 并且可以动态部署和管理 – 而不是在一台大型单机上整体运行。
- 资源隔离:可预测的应用程序性能。
- 资源利用:高效率和高密度
为什么需要 Kubernetes,它能做什么?
容器是打包和运行应用程序的好方式。在生产环境中, 你需要管理运行着应用程序的容器,并确保服务不会下线。 例如,如果一个容器发生故障,则你需要启动另一个容器。 如果此行为交由给系统处理,是不是会更容易一些? 这就是 Kubernetes 要来做的事情! Kubernetes 为你提供了一个可弹性运行分布式系统的框架。 Kubernetes 会满足你的扩展要求、故障转移你的应用、提供部署模式等。 例如,Kubernetes 可以轻松管理系统的 Canary (金丝雀) 部署。
Kubernetes相关概念总结
k8s中配置客户端访问pod中应用的流程如下:
client->ingress->service->pod->container
INGRESS
Ingress 是对集群中服务的外部访问进行管理的 API 对象,典型的访问方式是 HTTP。 Ingress 可以提供负载均衡、SSL 终结和基于名称的虚拟托管。
SERVICE
将运行在一组 Pods 上的应用程序公开为网络服务的抽象方法。Kubernetes Service 定义了这样一种抽象:逻辑上的一组 Pod,一种可以访问它们的策略 —— 通常称为微服务。 Service 所针对的 Pods 集合通常是通过选择算符来确定的。
POD
Pod 是可以在 Kubernetes 中创建和管理的、最小的可部署的计算单元。 Pod (就像在鲸鱼荚或者豌豆荚中)是一组(一个或多个) 容器; 这些容器共享存储、网络、以及怎样运行这些容器的声明。 Pod 中的内容总是并置(colocated)的并且一同调度,在共享的上下文中运行。 Pod 所建模的是特定于应用的“逻辑主机”,其中包含一个或多个应用容器, 这些容器是相对紧密的耦合在一起的。 在非云环境中,在相同的物理机或虚拟机上运行的应用类似于 在同一逻辑主机上运行的云应用。
节点(Node)
Kubernetes 集群中其中一台工作机器,是集群的一部分。
k8s-client-java选型
目前通过java操作k8s,开源版本共有两个:
kubernetes-client/java和fabric8io/kubernetes-client对比
| 和官网API一致性 | 社区活跃度 | 代码生成 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| kubernetes-client/java | 根据k8s-openapi随之更新,一致性和更新频率高 | 目前不活跃 | kubernetes-client/java提供了生成代码的通用跨语言工具,该工具托管在 kubernetes-client / gen存储库中 |
| fabric8io/kubernetes-client | 一致性低,更新慢;其中不支持k8s1.8和1.13 | 社区活跃,目前使用者多 | 暂无 |
鉴于kubernetes-client/java和官网API一致性好,本文决定采用它
2.环境部署
Download and run the installer for the latest release.
Or if using PowerShell, use this command:
1 2 | New-Item -Path 'c:' -Name 'minikube' -ItemType Directory -ForceInvoke-WebRequest -OutFile 'c:minikubeminikube.exe' -Uri 'https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/releases/latest/download/minikube-windows-amd64.exe' -UseBasicParsing |
Add the minikube.exe binary to your PATH.
Make sure to run PowerShell as Administrator.
1 2 3 4 | $oldPath = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path', [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine)if ($oldPath.Split(';') -inotcontains 'C:minikube'){[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('Path', $('{0};C:minikube' -f $oldPath), [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine)} |
If you used a terminal (like powershell) for the installation, please close the terminal and reopen it before running minikube
other plateform,
please visit at:https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/start/?arch=%2Fwindows%2Fx86-64%2Fstable%2F.exe+download
install kubectl
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl-windows/
Start your cluster
1 | minikube start |
Interact with your cluster
1 | kubectl get po -A |
Alternatively, minikube can download the appropriate version of kubectl and you should be able to use it like this:
1 | minikube kubectl -- get po -A |
You can also make your life easier by adding the following to your shell config: (for more details see: kubectl)
1 | alias kubectl="minikube kubectl --" |
Initially, some services such as the storage-provisioner, may not yet be in a Running state. This is a normal condition during cluster bring-up, and will resolve itself momentarily. For additional insight into your cluster state, minikube bundles the Kubernetes Dashboard, allowing you to get easily acclimated to your new environment:
1 | minikube dashboard |
3.代码工程
实验目标
- 实现java api获取pod信息
- 实现java api创建ingress
- 实现java api创建service
pom.xml
1 | springboot-democom.et1.0-SNAPSHOT4.0.0Kubernetes88org.springframework.bootspring-boot-starter-weborg.springframework.bootspring-boot-autoconfigureorg.springframework.bootspring-boot-starter-testtestio.kubernetesclient-java12.0.1compileorg.projectlomboklombok |
kubernetes工具类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 | package com.et.k8s.client;import io.kubernetes.client.custom.IntOrString;import io.kubernetes.client.openapi.ApiClient;import io.kubernetes.client.openapi.ApiException;import io.kubernetes.client.openapi.apis.CoreV1Api;import io.kubernetes.client.openapi.apis.ExtensionsV1beta1Api;import io.kubernetes.client.openapi.apis.NetworkingV1Api;import io.kubernetes.client.openapi.models.*;import io.kubernetes.client.util.ClientBuilder;import io.kubernetes.client.util.KubeConfig;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.Map;@Slf4jpublic class K8sClient { private ApiClient apiClient; /** * loading the in-cluster config, including: * 1. service-account CA * 2. service-account bearer-token * 3. service-account namespace * 4. master endpoints(ip, port) from pre-set environment variables */ public K8sClient() { try { this.apiClient = ClientBuilder.cluster().build(); } catch (IOException e) { log.error("build K8s-Client error", e); throw new RuntimeException("build K8s-Client error"); } } /** * loading the out-of-cluster config, a kubeconfig from file-system * * @param kubeConfigPath */ public K8sClient(String kubeConfigPath) { try { this.apiClient = ClientBuilder.kubeconfig(KubeConfig.loadKubeConfig(new FileReader(kubeConfigPath))).build(); } catch (IOException e) { log.error("read kubeConfigPath error", e); throw new RuntimeException("read kubeConfigPath error"); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("build K8s-Client error", e); throw new RuntimeException("build K8s-Client error"); } } /** * get all Pods * * @return podList */ public V1PodList getAllPodList() { // new a CoreV1Api CoreV1Api api = new CoreV1Api(apiClient); // invokes the CoreV1Api client try { V1PodList list = api.listPodForAllNamespaces(null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null); return list; } catch (ApiException e) { log.error("get podlist error:" + e.getResponseBody(), e); } return null; } /** * create k8s service * * @param namespace * @param serviceName * @param port * @param selector * @return */ public V1Service createService(String namespace, String serviceName, Integer port, Map selector) { V1Service svc = new V1ServiceBuilder() .withNewMetadata() .withName(serviceName) .endMetadata() .withNewSpec() .addNewPort() .withProtocol("TCP") .withPort(port) .withTargetPort(new IntOrString(port)) .endPort() .withSelector(selector) .endSpec() .build(); // Deployment and StatefulSet is defined in apps/v1, so you should use AppsV1Api instead of CoreV1API CoreV1Api api = new CoreV1Api(apiClient); V1Service v1Service = null; try { v1Service = api.createNamespacedService(namespace, svc, null, null, null); } catch (ApiException e) { log.error("create service error:" + e.getResponseBody(), e); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("create service system error:", e); } return v1Service; } /** * create k8s V1Ingress * * @param namespace * @param ingressName * @param annotations * @param path * @param serviceName * @param servicePort * @return */ public V1Ingress createV1Ingress(String namespace, String ingressName, Map annotations, String path, String serviceName, Integer servicePort) { //build ingress yaml V1Ingress ingress = new V1IngressBuilder() .withNewMetadata() .withName(ingressName) .withAnnotations(annotations) .endMetadata() .withNewSpec() .addNewRule() .withHttp(new V1HTTPIngressRuleValueBuilder().addToPaths(new V1HTTPIngressPathBuilder() .withPath(path) .withPathType("Prefix") .withBackend(new V1IngressBackendBuilder() .withService(new V1IngressServiceBackendBuilder() .withName(serviceName) .withPort(new V1ServiceBackendPortBuilder() .withNumber(servicePort).build()).build()).build()).build()).build()) .endRule() .endSpec() .build(); NetworkingV1Api api = new NetworkingV1Api(apiClient); V1Ingress v1Ingress = null; try { v1Ingress = api.createNamespacedIngress(namespace, ingress, null, null, null); } catch (ApiException e) { log.error("create ingress error:" + e.getResponseBody(), e); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("create ingress system error:", e); } return v1Ingress; } /** * create k8s ExtensionIngress * * @param namespace * @param ingressName * @param annotations * @param path * @param serviceName * @param servicePort * @return */ public ExtensionsV1beta1Ingress createExtensionIngress(String namespace, String ingressName, Map annotations, String path, String serviceName, Integer servicePort) { //build ingress yaml ExtensionsV1beta1Ingress ingress = new ExtensionsV1beta1IngressBuilder() .withNewMetadata() .withName(ingressName) .withAnnotations(annotations) .endMetadata() .withNewSpec() .addNewRule() .withHttp(new ExtensionsV1beta1HTTPIngressRuleValueBuilder().addToPaths(new ExtensionsV1beta1HTTPIngressPathBuilder() .withPath(path) .withBackend(new ExtensionsV1beta1IngressBackendBuilder() .withServiceName(serviceName) .withServicePort(new IntOrString(servicePort)).build()).build()).build()) .endRule() .endSpec() .build(); ExtensionsV1beta1Api api = new ExtensionsV1beta1Api(apiClient); ExtensionsV1beta1Ingress extensionsV1beta1Ingress = null; try { extensionsV1beta1Ingress = api.createNamespacedIngress(namespace, ingress, null, null, null); } catch (ApiException e) { log.error("create ingress error:" + e.getResponseBody(), e); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("create ingress system error:", e); } return extensionsV1beta1Ingress; }} |
以上只是一些关键代码,所有代码请参见下面代码仓库
代码仓库
- https://github.com/Harries/springboot-demo(Kubernetes)
4.测试
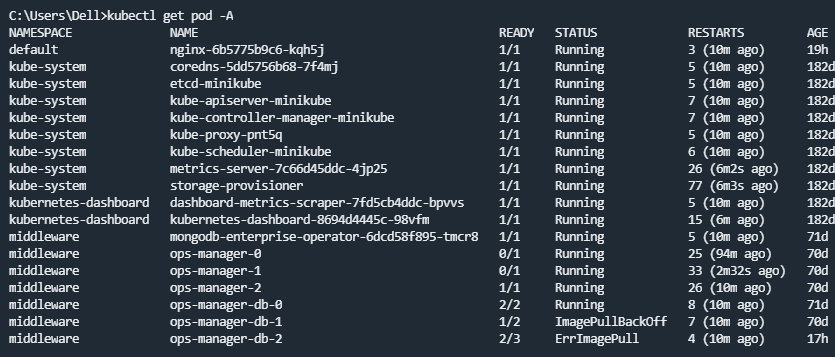
获取pods
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | @Testpublic void getAllPodListTest() { String kubeConfigPath = "C:\Users\Dell\.kube\config"; if (!new File(kubeConfigPath).exists()) { System.out.println("kubeConfig not exist,jump over"); return; } K8sClient k8sClient = new K8sClient(kubeConfigPath); V1PodList podList = k8sClient.getAllPodList(); for (V1Pod item : podList.getItems()) { System.out.println(item.getMetadata().getNamespace() + ":" + item.getMetadata().getName()); }} |
输出结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | default:nginx-6b5775b9c6-kqh5jkube-system:coredns-5dd5756b68-7f4mjkube-system:etcd-minikubekube-system:kube-apiserver-minikubekube-system:kube-controller-manager-minikubekube-system:kube-proxy-pnt5qkube-system:kube-scheduler-minikubekube-system:metrics-server-7c66d45ddc-4jp25kube-system:storage-provisionerkubernetes-dashboard:dashboard-metrics-scraper-7fd5cb4ddc-bpvvskubernetes-dashboard:kubernetes-dashboard-8694d4445c-98vfmmiddleware:mongodb-enterprise-operator-6dcd58f895-tmcr8middleware:ops-manager-0middleware:ops-manager-1middleware:ops-manager-2middleware:ops-manager-db-0middleware:ops-manager-db-1middleware:ops-manager-db-2 |
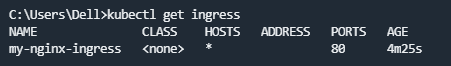
创建Ingress
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | @Testpublic void createV1IngressTest() { String kubeConfigPath = "C:\Users\Dell\.kube\config"; if (!new File(kubeConfigPath).exists()) { System.out.println("kubeConfig not exist,jump over"); return; } K8sClient k8sClient = new K8sClient(kubeConfigPath); String namespace = "default"; String ingressName = "my-nginx-ingress"; Map annotations = new HashMap(); annotations.put("nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target", "/"); String path = "/my-nginx"; String serviceName = "my-nginx-service"; Integer servicePort = 80; V1Ingress v1Ingress = k8sClient.createV1Ingress(namespace, ingressName, annotations, path, serviceName, servicePort); System.out.println(v1Ingress != null ? v1Ingress.getMetadata() : null);} |
创建Service
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | @Testpublic void createServiceTest() { String kubeConfigPath = "C:\Users\Dell\.kube\config"; if (!new File(kubeConfigPath).exists()) { System.out.println("kubeConfig not exist,jump over"); return; } K8sClient k8sClient = new K8sClient(kubeConfigPath); String namespace = "default"; String serviceName = "my-nginx-service"; Integer port = 80; Map selector = new HashMap(); selector.put("run", "my-nginx"); V1Service v1Service = k8sClient.createService(namespace, serviceName, port, selector); System.out.println(v1Service != null ? v1Service.getMetadata() : null);} |
5.引用
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl-windows/
- http://www.liuhaihua.cn/archives/711229.html
到此这篇关于Spring Boot集成kubernetes客户端实现API操作k8s集群的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring Boot集成kubernetes内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

