加载测试专用的属性
点开@SpringBootTest源码中查看
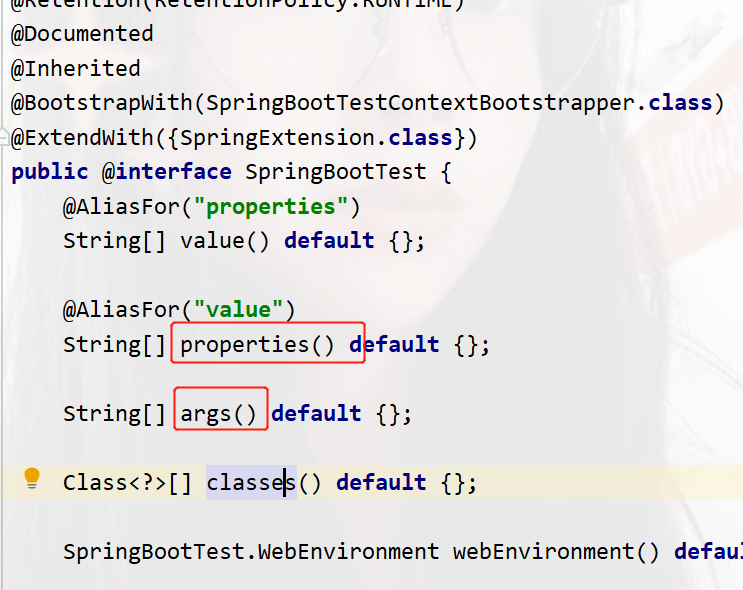
可以在之后加入临时配置, 也可以使用命令行args参数设置。设置的测试专用参数会覆盖配置文件中的。
package com;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
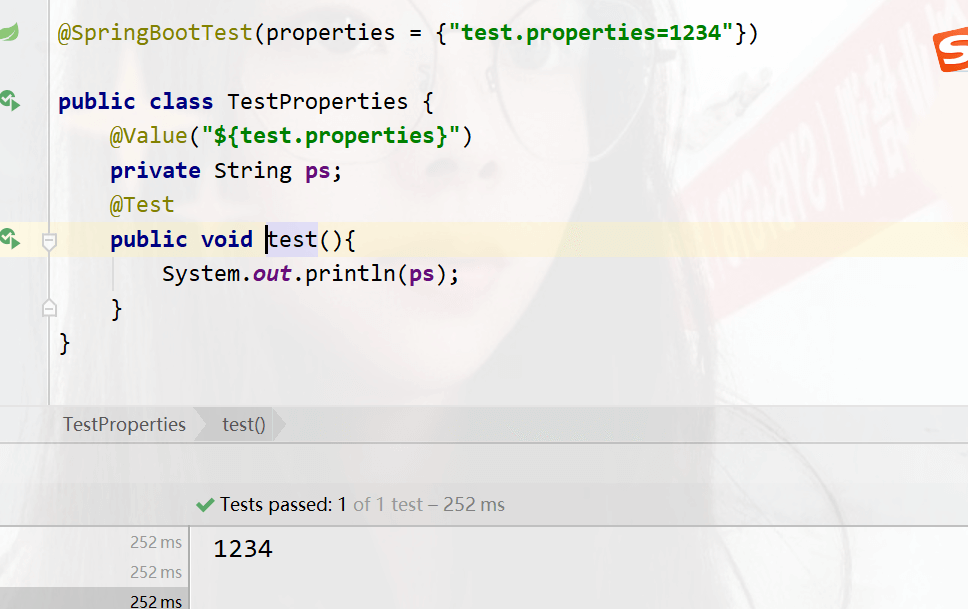
@SpringBootTest(args = {properties = {"test.properties=1234"})
public class TestProperties {
@Value("${test.properties}")
private String ps;
@Test
public void test(){
System.out.println(ps);
}
}
运行结果
也可以使用命令行参数
args = {“–test.properties=4321”},
命令行参数的优先级比配置文件的高,所以当两者共存的时候,以命令行的为主
@SpringBootTest(args = {"--test.properties=4321"},properties = {"test.properties=1234"})
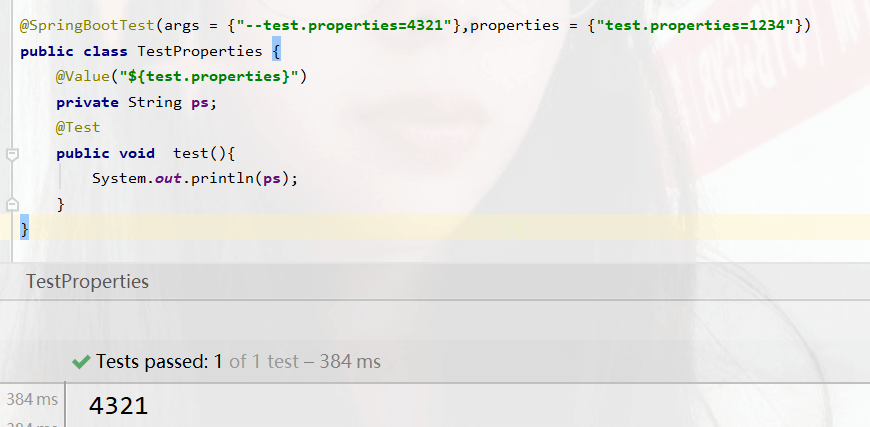
这个测试类设置的属性只对当前测试有效,影响小
使用外部bean对测试
package com.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration//说明当前为配置类
public class TestBean {
@Bean//创建bean
public String mess(){
return "this bean run ";
}
}
在测试类下,使用@Import注解加载当前测试配置
package com.test;
import com.config.TestBean;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@SpringBootTest
@Import({TestBean.class})
public class TestBeanNow {
@Autowired//注入bean对象
public String mess;
@Test
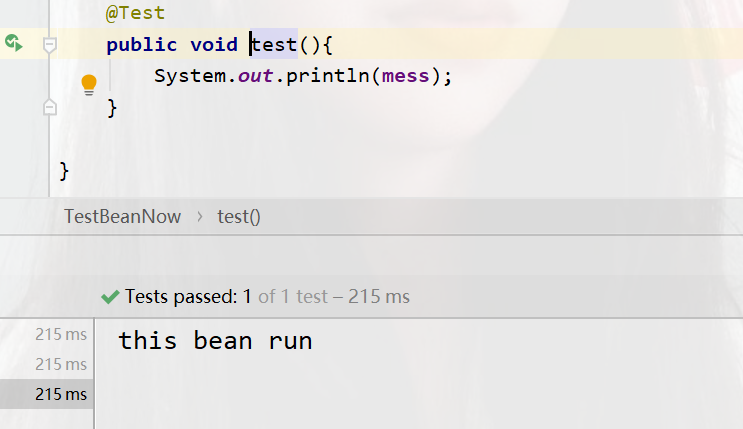
public void test(){
System.out.println(mess);
}
}
运行结果
测速类启动web环境
在测试类中运行一般是不会启动服务器的,如下图。都是显示运行成功或失败的信息
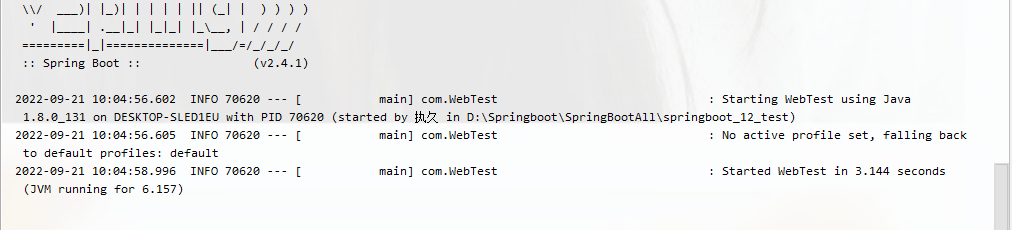
我们Ctrl+b点进@SpringBootTest源码中查看,有一个关于web的
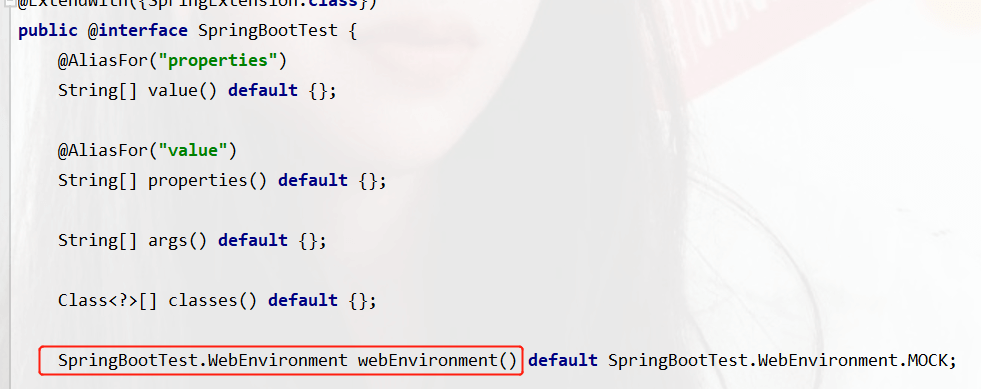
默认值是MOCK,mock:默认提供一个模拟的web环境,不会启动内嵌的服务器
我们在测试类中
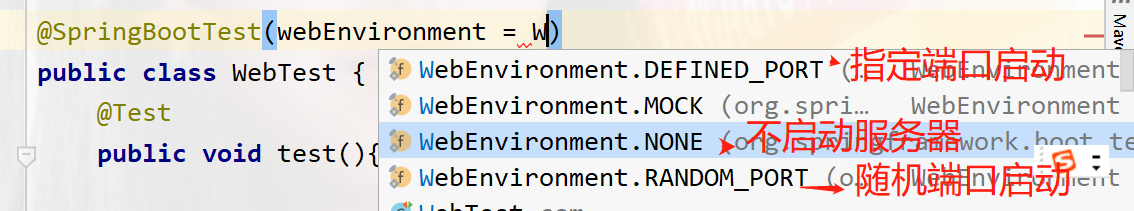
第一个是以你配置文件指定的端口启动,如果没有就默认以8080启动
第二个mock:默认提供一个模拟的web环境,不会启动内嵌的服务器
第三个是不启动服务器
第四个是随机端口启动
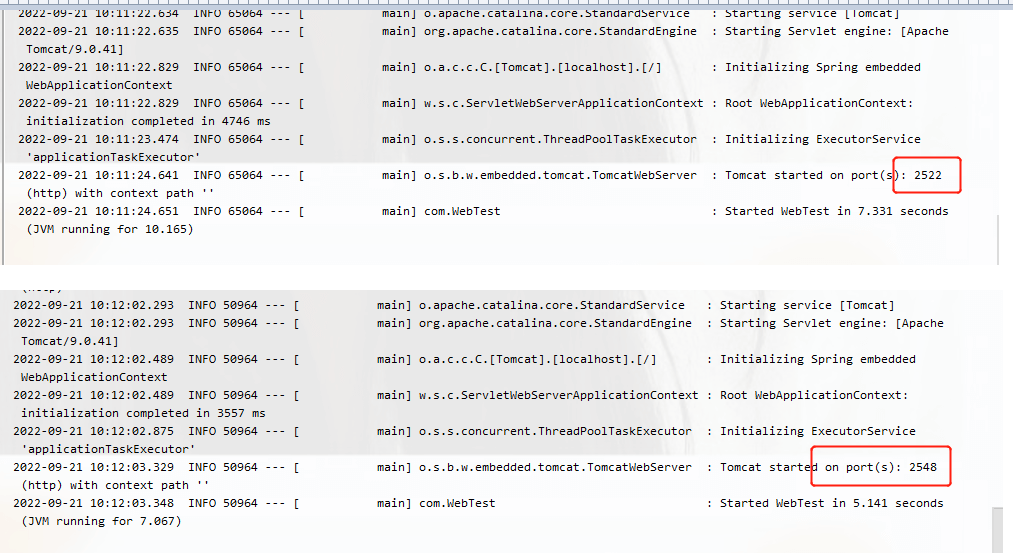
我们测试随机端口启动
package com;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class WebTest {
@Test
public void test(){
}
}
运行结果
运行了两次看端口结果,都是随机的
到此这篇关于SpringBoot测试配置属性与web启动环境超详细图解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot测试配置属性内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

