前言
本节我总结结合Lambda表达式使用的方法引用,本质上还是Lambda表达式!
什么是方法引用
当要传递给 Lambda 体的操作,已经有实现的方法了,可以使用方法引用!
方法引用可以看做是 Lambda 表达式深层次的表达。换句话说,方法引用就是 Lambda 表达式,也就是函数式接口的一个实例,通过方法的名字来指向一个方法,可以认为是 Lambda 表达式的一个语法糖。
要求:实现接口的抽象方法的参数列表和返回值类型,必须与方法引用的方法的参数列表和返回值类型保持一致!
格式:使用操作符”::”将类(或对象)与方法名分隔开来。
有如下三种主要使用情况:
- >对象::实例方法名
- >类::静态方法名
- >类::实例方法名
方法引用的三种情况案例
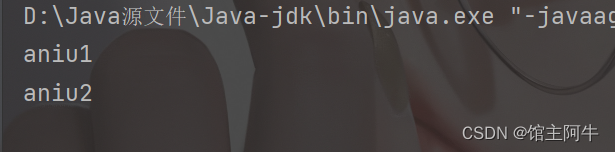
情况一:对象::实例方法名
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | public static void main(String[] args) { // 情况一:对象::实例方法名 // Consumer 中的 void accept(T t) // void accept(T t) 与 打印流中的void println(T t) 参数类型和返回值一致,因此可以用方法引用 // Lambda 表达式 Consumer con1 = str -> System.out.println(str); con1.accept("aniu1"); // 方法引用改写 PrintStream ps = System.out; //对象::实例方法名 Consumer con2 = ps::println; con2.accept("aniu2"); } |
情况二:类::静态方法名
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | // 情况二:类::静态方法 // Comparator 中的 int compare(T t1,T t2) // int compare(T t1,T t2) 与 Integer中的int compare(T t1,T t2) 参数类型和返回值一致,因此可以用方法引用 // Lambda 表达式 Comparator com3 = (t1,t2) -> Integer.compare(t1,t2); System.out.println(com3.compare(12, 21)); // 方法引用改写 Comparator com4 = Integer::compare; System.out.println(com4.compare(12, 21)); |
情况三:类::实例方法名
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | // 情况三:类::实例方法名 (有难度)---前面方法引用的要求针对的是情况一和情况二,对情况三不适用 // Comparator 中的 int compare(T t1,T t2) // String 中的 int t1.compareTo(t2) // T t1 作为compareTo的调用者,T的类型作为 类::实例方法名 中的类 // Lambda 表达式 Comparator com5 = (s1,s2) -> s1.compareTo(s2); System.out.println(com5.compare("A", "B")); // 方法引用改写 Comparator com6 = String::compareTo; System.out.println(com6.compare("A", "B")); |
这一块还是比较抽象的,多去理解,我不在多举例子!
构造器引用
和方法引用类似,函数式接口的抽象方法的形参列表和构造器的形参列表一致,抽象方法的返回值类型即为构造器所属的类的类型!
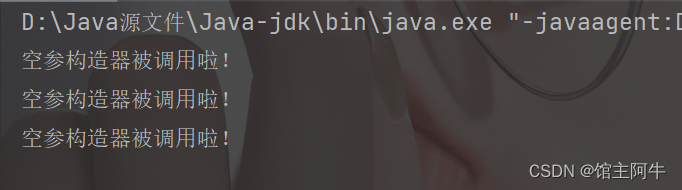
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | package 构造器引用;import java.util.function.Supplier;/** * @Author:Aniu * @Date:2023/2/23 21:33 * @description TODO */public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 原始写法 Supplier sup1 = new Supplier() { @Override public People get() { return new People(); } }; sup1.get(); // Lambda 表达式 Supplier sup2 = () -> new People(); sup2.get(); // 构造器引用 // Supplier中的T get() // People 的空参构造器 People() Supplier sup3 = People::new; sup3.get(); }}class People{ String name; int age; public People(){ System.out.println("空参构造器被调用啦!"); } public People(int a){ this.age = a; System.out.println("有参构造器被调用啦!"); }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | // Lambda 表达式 Function fun1 = id -> new People(id); fun1.apply(18); // 构造器引用 // Function 中的R apply(T t) // 函数式接口 // People 的有参构造器 People(T t) Function fun4 = People::new; fun1.apply(18); |

还有数组引用,这里不再总结,感兴趣的可以去了解!
到此这篇关于一文详解Java8中的方法引用与构造器引用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java8方法引用 构造器引用内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

