前言
在 Python 中,打开文件时需要指定打开文件的模式。常见的文件打开模式包括:
-
‘r’:读取模式。默认模式,用于读取文件内容。如果文件不存在,则会引发
FileNotFoundError错误。 -
‘w’:写入模式。如果文件不存在,则创建文件;如果文件已存在,则先清空文件内容,然后写入新内容。
-
‘a’:追加模式。用于在文件末尾添加新内容,而不会影响原有内容。如果文件不存在,则创建文件。
打开文件并读取内容
with open("./data/example.txt", "r",encoding="utf-8") as file:
content = file.read()
print(content)
写入内容到文件
with open("./data/example.txt", "w") as file:
file.write("Hello, World!")
逐行读取文件内容
with open("./data/example.txt", "r") as file:
for line in file:
print(line)
追加内容到文件
with open("./data/example.txt", "a") as file:
file.write("nAppending new line!")
文件重命名
import os
os.rename("./data/example.txt", "./data/new_example.txt")
文件删除
import os
os.remove("./data/example.txt")
检查文件是否存在
import os
if os.path.exists("./data/example.txt"):
print("文件存在")
else:
print("文件不存在")
创建文件目录
import os
os.mkdir("example_directory")
删除文件目录
import os
os.rmdir("example_directory")
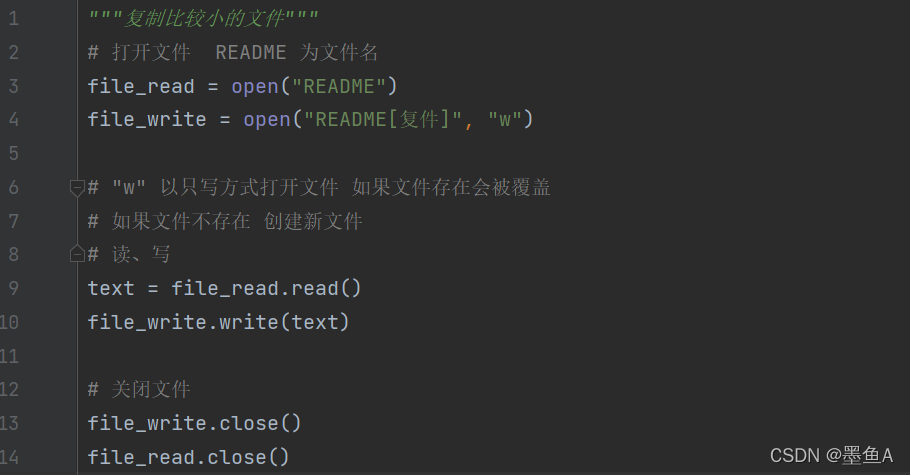
复制文件
两种方式:
第一种方法适合复制比较小的文件
第二种方式适合复制比较大的文件

总结
到此这篇关于Python文件操作命令的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python文件操作命令内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

