前言
- 在PyQt5中,GUI线程通常指的是Qt的主事件循环线程,也称为主线程。主线程负责处理GUI事件、更新UI界面等任务。在PyQt5中,主线程和GUI线程是同一个线程,即运行应用程序的线程。
- 当创建一个Qt应用程序时,主线程会启动,并执行QApplication.exec_()方法,进入Qt的事件循环。在事件循环中,主线程会不断地监听并处理用户的输入事件、定时器事件、网络事件等,然后更新UI界面。
- 如果在主线程执行耗时操作,比如
循环、sleep、wait 异步线程执行会导致 UI 界面进入无响应状态,我们可以采用以下两种方式异步处理:使用QThread 或 QTimer。
版本
- PyQt5
- Python 3.x
案例
- 我们写一个简单的进度条填充程序,每 2 秒填充 1%:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | import sysimport timefrom PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QProgressBar, QPushButton, QHBoxLayoutclass MyWidget(QWidget): def __init__(self): super(MyWidget, self).__init__() self.currentValue = 0 self.progressBar = QProgressBar(self) self.progressBar.resize(200, 50) self.progressBar.move(20, 20) self.progressBar.setValue(self.currentValue) # 创建一个按钮 self.button = QPushButton('点击我', self) self.button.clicked.connect(self.on_clicked) # 创建一个垂直布局,并将按钮添加到布局中 layout = QHBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.progressBar) layout.addWidget(self.button) # 设置窗口的主布局为垂直布局 self.setLayout(layout) def on_clicked(self): while True: time.sleep(2) self.currentValue = (self.currentValue + 1) % 101 self.progressBar.setValue(self.currentValue)if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) w = MyWidget() w.resize(500, 300) w.move(300, 300) w.setWindowTitle('Simple') w.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) |
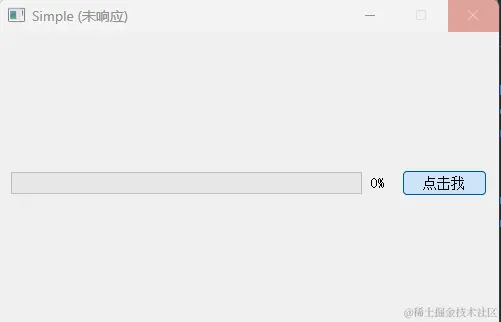
- 点击运行,我们会发现 UI 界面出现无响应且进度条没有刷新:
解决方案
- 为了避免 UI 界面无响应,我们可以采用以下两种方式:使用
QThread 或 QTimer。
QThread
- 我们可以通过点击事件创建
QThread异步线程执行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 | import sysimport timefrom PyQt5.QtCore import QThread, pyqtSignalfrom PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QProgressBar, QPushButton, QHBoxLayoutclass MyWorker(QThread): timeout = pyqtSignal() def __init__(self): super(MyWorker, self).__init__() def run(self): while True: time.sleep(2) self.timeout.emit()class MyWidget(QWidget): def __init__(self): super(MyWidget, self).__init__() self.worker = None self.currentValue = 0 self.progressBar = QProgressBar(self) self.progressBar.resize(200, 50) self.progressBar.move(20, 20) self.progressBar.setValue(self.currentValue) # 创建一个按钮 self.button = QPushButton('点击我', self) self.button.clicked.connect(self.on_clicked) # 创建一个垂直布局,并将按钮添加到布局中 layout = QHBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.progressBar) layout.addWidget(self.button) # 设置窗口的主布局为垂直布局 self.setLayout(layout) def on_clicked(self): self.worker = MyWorker() self.worker.timeout.connect(self.upgradeProgress) self.worker.start() def upgradeProgress(self): self.currentValue = (self.currentValue + 1) % 101 self.progressBar.setValue(self.currentValue)if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) w = MyWidget() w.resize(500, 300) w.move(300, 300) w.setWindowTitle('Simple') w.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) |
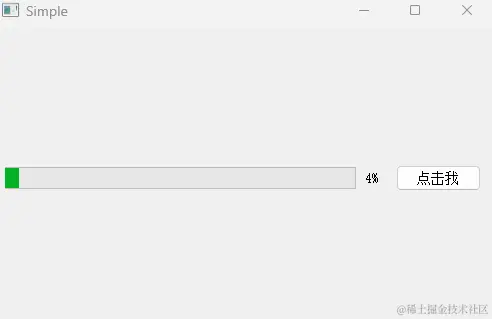
运行效果:
QTimer
- 我们可以通过点击事件创建
QTimer定时器异步执行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 | import sysfrom PyQt5.QtCore import QTimerfrom PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QProgressBar, QPushButton, QHBoxLayoutclass MyWidget(QWidget): def __init__(self): super(MyWidget, self).__init__() self.currentValue = 0 self.progressBar = QProgressBar(self) self.progressBar.resize(200, 50) self.progressBar.move(20, 20) self.progressBar.setValue(self.currentValue) # 创建一个按钮 self.button = QPushButton('点击我', self) self.button.clicked.connect(self.on_clicked) # 创建一个垂直布局,并将按钮添加到布局中 layout = QHBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.progressBar) layout.addWidget(self.button) # 设置窗口的主布局为垂直布局 self.setLayout(layout) def on_clicked(self): # 定义一个定时器并启动定时器 self.time = QTimer() self.time.timeout.connect(self.upgradeProgress) self.time.start(200) def upgradeProgress(self): self.currentValue = (self.currentValue + 1) % 101 self.progressBar.setValue(self.currentValue)if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) w = MyWidget() w.resize(500, 300) w.move(300, 300) w.setWindowTitle('Simple') w.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) |
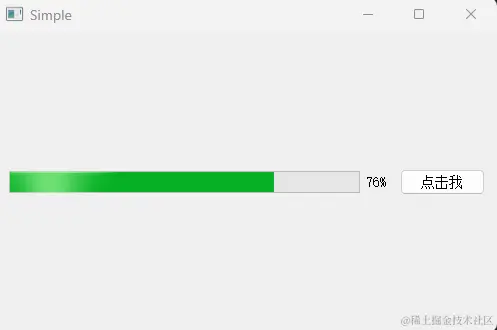
- 运行效果:
局部变量创建异步线程导致 UI 未响应
- 在使用
QThread的案例中,将on_clicked方法改为如下写法,同样会导致 UI 未响应状态:
1 2 3 4 | def on_clicked(self): worker = MyWorker() worker.timeout.connect(self.upgradeProgress) worker.start() |
- 这是因为在Python中,类似于
worker = MyWorker()这样的语句创建的对象在当前作用域中是局部变量,它的生命周期与当前作用域相关联。当当前作用域的代码执行完成后局部变量会被销毁。 - 如果异步线程的任务还没有完成,而主线程的事件循环又需要等待任务完成才能继续执行,那么就会导致GUI线程无响应。这是因为主线程被阻塞在等待异步任务的过程中,无法处理事件。
- 为了避免这种情况,我们应该将异步线程对象存储为实例变量(即使用
self.worker = MyWorker()),这样可以确保异步线程对象的生命周期与主对象相同,直到异步任务完成。这样即使当前作用域的代码执行完成,异步线程仍然可以继续执行,并且主线程的事件循环也不会被阻塞。
如果 QTimer 不使用 self.time 写法
- 同理,如果不使用
self.time写法,会被当做当前作用域中的局部变量,当前作用域代码执行完成后就会被销毁,不再继续执行。
到此这篇关于PyQt5界面无响应的解决方案的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关PyQt5界面无响应内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

