前言
假设我们给锁设置的过期时间太短,业务还没执行完成,锁就过期了,这块应该如何处理呢?是否可以给分布式锁续期?
解决方案:先设置一个过期时间,然后我们开启一个守护线程,定时去检测这个锁的失效时间,如果锁快要过期了,操作共享资源还未完成,那么就自动对锁进行续期,重新设置过期时间。
幸运的是有一个库把这些工作都帮我们封装好了,那就是 Redisson,Redisson 是 java 语言实现的 Redis SDK 客户端,它能给 Redis 分布式锁实现过期时间自动续期。
当然,Redisson 不只是会做这个,除此之外,还封装了很多易用的功能:
- 可重入锁
- 乐观锁
- 公平锁
- 读写锁
- Redlock
这里我们只讲怎么实现续期,有需要的小伙伴可以自己去了解其他的功能哦。
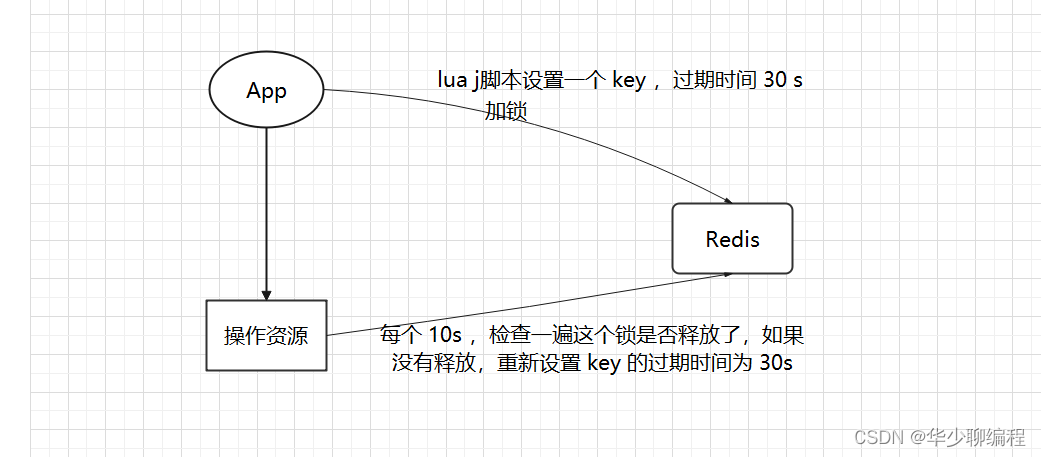
在使用分布式锁时,Redisson 采用了自动续期的方案来避免锁过期,这个守护线程我们一般也把它叫做 “看门狗(watch dog)” 线程。
watch dog自动延期机制
只要客户端一旦加锁成功,就会启动一个 watch dog 看门狗。watch dog 是一个后台线程,会每隔 10 秒检查一下,如果客户端还持有锁 key,那么就会不断的延长锁 key 的生存时间。
如果负责存储这个分布式锁的 Redission 节点宕机后,而且这个锁正好处于锁住的状态时,这个锁会出现锁死的状态,为了避免这种情况的发生,Redisson 提供了一个监控锁的看门狗,它的作用是在 Redisson 实例被关闭前,不断的延长锁的有效期。默认情况下,看门狗的续期时间是 30 秒,也可以通过修改 Config.lockWatchdogTimeout 来指定。
另外 Redisson 还提供了可以指定 leaseTime 参数的加锁方法来指定加锁的时间。超过这个时间后锁便自动解开了,不会延长锁的有效期。
接下来我们从源码看一下是怎么实现的。
源码分析
首先我们先写一个 dome 一步步点击进去看。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | Config config = new Config(); config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379"); RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config); RLock lock = redisson.getLock("MyLock"); lock.lock(); |
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(“MyLock”); 这句代码就是为了获取锁的实例,然后我们可以看到它返回的是一个 RedissonLock 对象
1 2 3 4 5 | //name:锁的名称public RLock getLock(String name) {//默认创建的同步执行器, (存在异步执行器, 因为锁的获取和释放是有强一致性要求, 默认同步) return new RedissonLock(this.connectionManager.getCommandExecutor(), name);} |
点击 RedissonLock 进去,发现这是一个 RedissonLock 构造方法,主要初始化一些属性。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | public RedissonLock(CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor, String name) { super(commandExecutor, name); this.commandExecutor = commandExecutor; //唯一ID this.id = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getId(); //等待获取锁时间 this.internalLockLeaseTime = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(); //ID + 锁名称 this.entryName = this.id + ":" + name; //发布订阅 this.pubSub = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getSubscribeService().getLockPubSub();} |
我们点击 getLockWatchdogTimeout() 进去看一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | public class Config { private long lockWatchdogTimeout = 30 * 1000; public long getLockWatchdogTimeout() { return lockWatchdogTimeout; } //省略} |
从 internalLockLeaseTime 这个单词也可以看出,这个加的分布式锁的超时时间默认是 30 秒,现在我们知道默认是 30 秒,那么这个看门狗多久时间来延长一次有效期呢?我们接着往下看。
这里我们选择 lock.lock(); 点击进去看:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | public void lock() { try { this.lock(-1L, (TimeUnit)null, false); } catch (InterruptedException var2) { throw new IllegalStateException(); }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | private void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, boolean interruptibly) throws InterruptedException { long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId(); Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId); if (ttl != null) { RFuture future = this.subscribe(threadId); if (interruptibly) { this.commandExecutor.syncSubscriptionInterrupted(future); } else { this.commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future); } |
上面参数的含义:
leaseTime: 加锁到期时间, -1 使用默认值 30 秒
unit: 时间单位, 毫秒、秒、分钟、小时…
interruptibly: 是否可被中断标示
而 this.tryAcquire()这个方法中是用来执行加锁, 继续跳进去看:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | private RFuture tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) { //执行 tryLock(...) 才会进入 if (leaseTime != -1L) { //进行异步获取锁 return this.tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG); } else { //尝试异步获取锁, 获取锁成功返回空, 否则返回锁剩余过期时间 RFuture ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG); //ttlRemainingFuture 执行完成后触发此操作 ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> { if (e == null) { //ttlRemaining == null 代表获取了锁 //获取到锁后执行续时操作 if (ttlRemaining == null) { this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId); } } }); return ttlRemainingFuture; }} |
我们继续选择 scheduleExpirationRenewal() 跳进去看:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) { RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry entry = new RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry(); RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry oldEntry = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(this.getEntryName(), entry); if (oldEntry != null) { oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId); } else { entry.addThreadId(threadId); this.renewExpiration(); }} |
接着进去 renewExpiration() 方法看:
该方法就是开启定时任务,也就是 watch dog 去进行锁续期。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | private void renewExpiration() { //从容器中去获取要被续期的锁 RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ee = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(this.getEntryName()); //容器中没有要续期的锁,直接返回null if (ee != null) { //创建定时任务 //并且执行的时间为 30000/3 毫秒,也就是 10 秒后 Timeout task = this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() { public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception { //从容器中取出线程 RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ent = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)RedissonLock.EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(RedissonLock.this.getEntryName()); if (ent != null) { Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId(); if (threadId != null) { //Redis进行锁续期 //这个方法的作用其实底层也是去执行LUA脚本 RFuture future = RedissonLock.this.renewExpirationAsync(threadId); //同理去处理Redis续命结果 future.onComplete((res, e) -> { if (e != null) { RedissonLock.log.error("Can't update lock " + RedissonLock.this.getName() + " expiration", e); } else { //如果成功续期,递归继续创建下一个 10S 后的任务 if (res) { //递归继续创建下一个10S后的任务 RedissonLock.this.renewExpiration(); } } }); } } } }, this.internalLockLeaseTime / 3L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); ee.setTimeout(task); }} |
从这里我们就知道,获取锁成功就会开启一个定时任务,也就是 watchdog 看门狗,定时任务会定期检查去续期renewExpirationAsync(threadId)。
从这里我们明白,该定时调度每次调用的时间差是 internalLockLeaseTime / 3,也就是 10 秒。
总结
面试的时候简单明了的回答这个问题就是:
只要客户端一旦加锁成功,就会启动一个 watch dog 看门狗,他是一个后台线程,会每隔 10 秒检查一下,如果客户端还持有锁 key,那么就会不断的延长锁 key 的过期时间。
默认情况下,加锁的时间是 30 秒,.如果加锁的业务没有执行完,就会进行一次续期,把锁重置成 30 秒,万一业务的机器宕机了,那就续期不了,30 秒之后锁就解开了。
到此这篇关于Redis锁的过期时间小于业务的执行时间如何续期的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Redis 锁续期内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

